🎯 Week 8 - Web 3 basics for Product Managers
Quote
Everything will be tokenized and connected by a blockchain one day. – Fred Ehrsam
💯 Framework // Concept // Mental Model
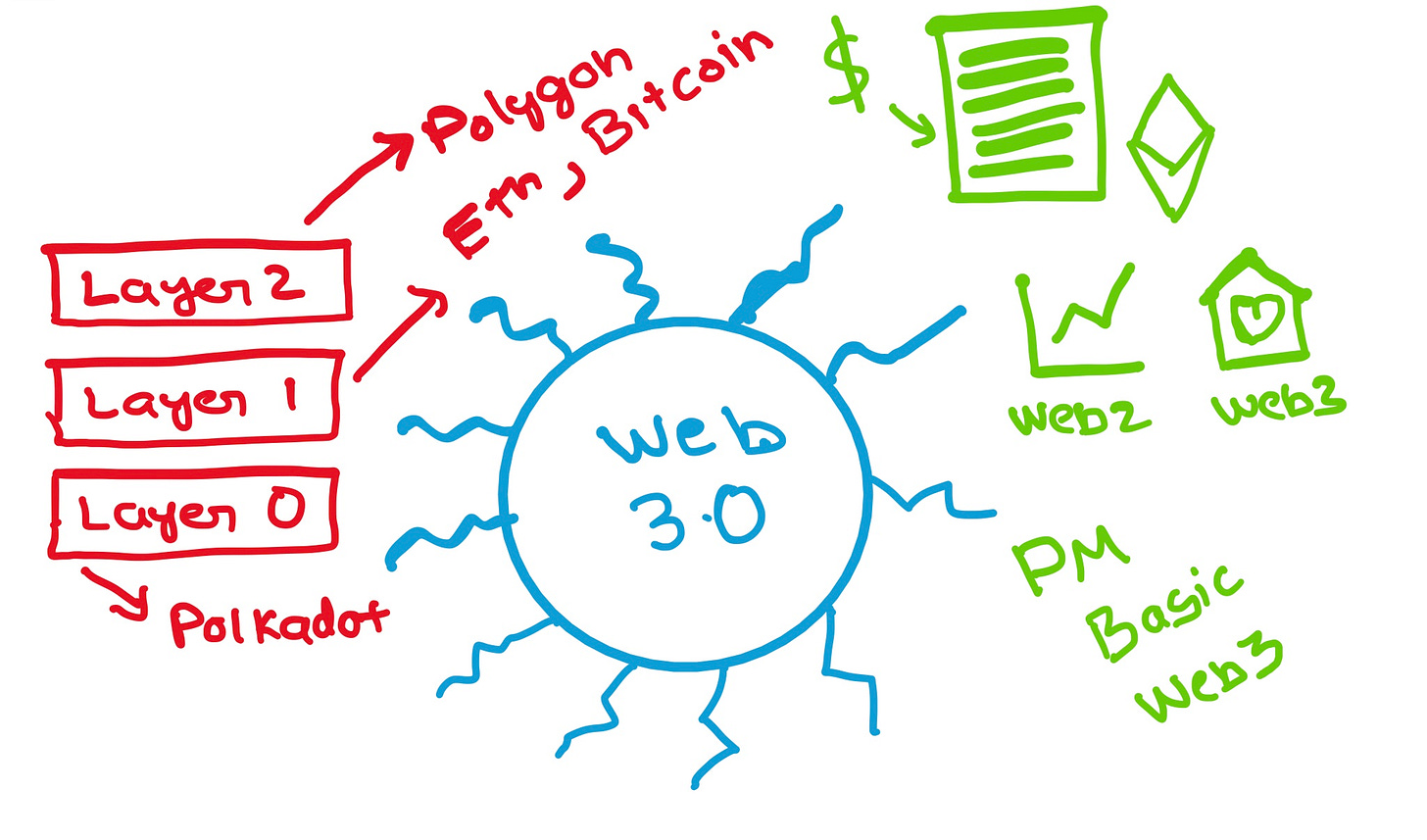
A comprehensive guide to understanding crypto and blockchain for product managers
The third generation of the internet, or Web 3, is being built on a new set of technologies that have the potential to change the way we use the int…
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to The Product Channel By Sid Saladi to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.